07/05/18 giovanni 0 0

study of the motion in presence of constant acceleration
Developed by Margaux Khalil (École Estienne), Julien Bobroff and Frédéric Bouquet (Laboratoire de Physique des solides, Université Paris-Sud and CNRS). More information and other projects on opentp.fr/en


 Level : Medium
Level : Medium
 1 day
1 day
The objective is to measure the relation between velocity and acceleration

The physic in action
For an constantly accelerated motion, the relation between velocity and accelerationis given by :
V_{final}-V_{initial} = a(t_{final}-t_{initial})
Measuring the variation of velocity with time gives the acceleration.
-
 Connecting wires
Connecting wires
-
 Legos
Legos
-
 Tinkering tools
Tinkering tools
-
 Breadboard
Breadboard
-
 Arduino
Arduino
-
 ultrasonic sensor (HC-SR40)
ultrasonic sensor (HC-SR40)
Material
The ultrasonic HC-SR40 measures the distance by measuring the echo time of an ultrasonic pulse.

Step 1
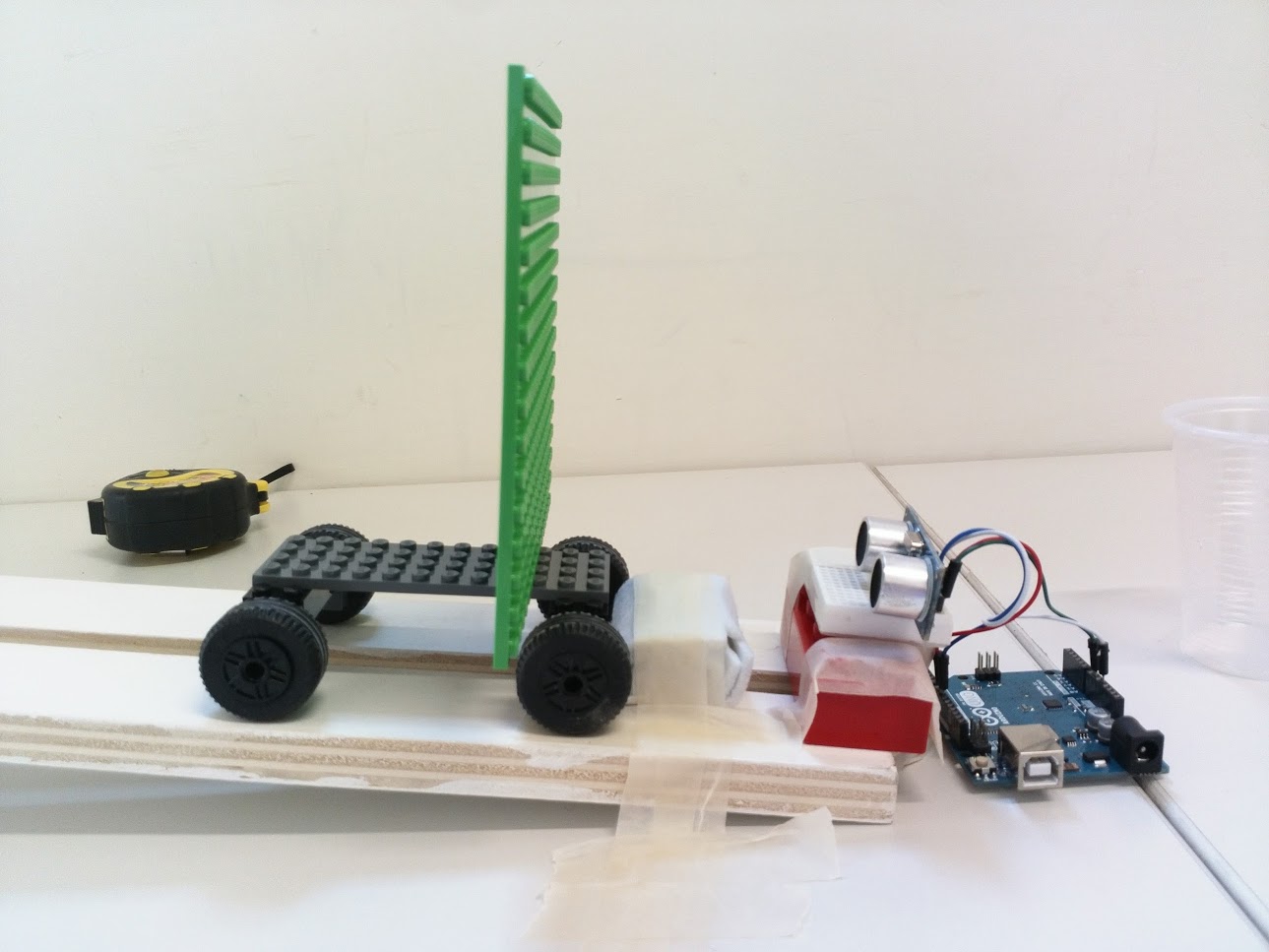
Build an inclined plane, and fix the ultrasonic sensor at the end of the plane.
Build a lego car; it should be big enough to produce an echo to the sensor.

Step 2
Connect your sensor to your Arduino board. You can find various tutorials on how to do so on the Internet.

Program the Arduino board so that the velocity of the lego car can be measured, by comparing the position of the car at two different times.
Mind the units…

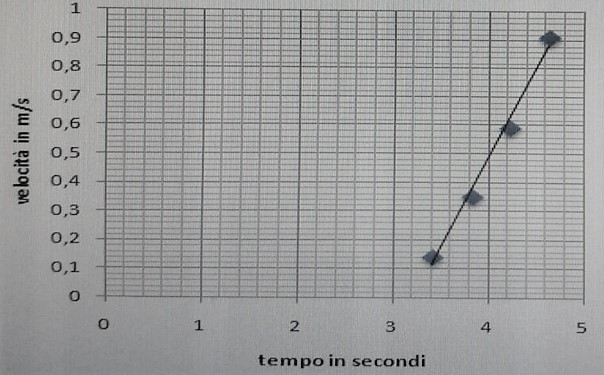
What is the variation of the velocity with time when the car rolls down the inclined plane?
What is the variation of the acceleration with time?

Can a simple point like particle mechanical model explain your measurements?
Step 4
Plot your data, and determine the precision of your results.
This experiment was made during the “School of physics with Arduino and smartphones” held in Rome for high school physics teachers in September 2016 by Federica Camilli, Paola Mamone, and Gabriella Pulvirenti
http://www.phys.uniroma1.it/fisica/scuola-arduino-Prima_edizione





comments